
For example, a company performs landscaping services in theamount of $1,500. Atthe period end, the company would record the following adjustingentry. Depreciation may also require an adjustment at the end of theperiod. Recall that depreciation isthe systematic method to record the allocation of cost over a givenperiod of certain assets. This allocation of cost is recorded overthe useful life of the asset, or the time periodover which an asset cost is allocated.
Bad Debts Expense
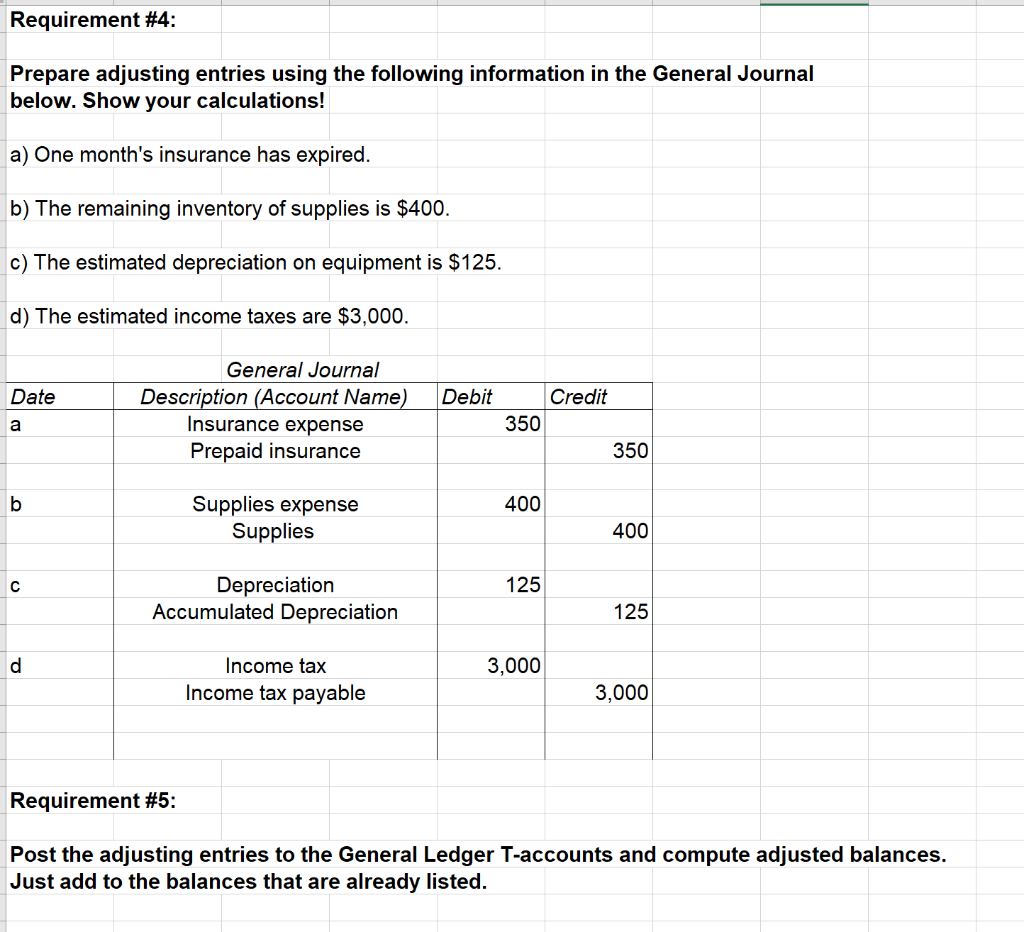
- Following our year-end example of Paul’s Guitar Shop, Inc., we can see that his unadjusted trial balance needs to be adjusted for the following events.
- Accrued expenses are expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid.
- Retainer fees are money lawyers collect in advance of starting work on a case.
- In the journal entry, Depreciation Expense–Equipment has a debitof $75.
- The life of a business is divided into accounting periods, which is the time frame (usually a fiscal year) for which a business chooses to prepare its financial statements.
- To learn more about the balance sheet, see our Balance Sheet Outline.
Each month that passes, the company needs to record rentused for the month. Depreciation Expense increases (debit) and AccumulatedDepreciation, Equipment, increases (credit). If the company wantedto compute the book value, it would take the original cost of theequipment and subtract accumulated depreciation. The required adjusting entries depend on what types oftransactions the company has, but there are some common types ofadjusting entries.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
The following entries show initial payment for four months of rent and the adjusting entry for one month’s usage. In October, cash is recorded into accounts receivable as cash expected to be received. Then when the client sends payment in December, it’s time to make the adjusting entry. Fees earned from providing services and the amounts of merchandise sold.
What is an example of an adjusting entry?
Previously unrecorded service revenue can arise when a companyprovides a service but did not yet bill the client for the work.This means the customer has also not yet paid for services. Sincethere was no bill to trigger a transaction, an adjustment isrequired to recognize revenue earned at the end of the period. For example, let’s say a company pays $2,000 for equipment thatis supposed to last four years.
This category of adjusting entries is also known as unearned income, deferred revenue, or deferred income. Essentially, it refers to money you’ve been prepaid by a client before you’ve done the work or provided services. In the accrual system, this unearned income is seen as a liability and should be credited.
Adjusting Entry for Accrued Expense
The same is true about just about any asset youcan name, except, perhaps, cash itself. Journal entries are recorded when an activity or event occursthat triggers the entry. Recall that an original source can be a formal documentsubstantiating a transaction, such as an invoice, purchase order,cancelled check, or employee time sheet. Not every transactionproduces an original source document that will alert the bookkeeperthat it is time to make an entry. The number and variety of adjustments needed at the end of the accounting period differ depending on the size and nature of the business.
Salaries Payable has a credit balance of $1,500.This is posted to the Salaries Payable T-account on the credit side(right side). Thisis posted to the Supplies Expense T-account on the debit side (leftside). This is posted to theSupplies T-account on the credit side (right side). You will noticethere is already a debit balance in this account from the purchaseof supplies on January 30. The $100 is deducted from $500 to get afinal debit balance of $400. The adjustment entry is then recorded in the general ledger using the appropriate accounts and amounts.
Most accounting software has built-in features that allow for the easy creation and recording of adjustment entries. The revenue recognition principle requires businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received. Adjustment entries are necessary to ensure that revenue is recognized in the correct period, even if payment has not been received. Amortization is the allocation of the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. To record amortization, an accountant would debit an expense account and credit an accumulated amortization account.
However, mistakes can happen, and it is crucial to avoid them to ensure accurate financial statements. Understanding adjustment entries is critical for anyone involved in accounting, finance, or business operations. There when are adjusting entries prepared are several types of adjustment entries, including accruals, deferrals, estimates, and reclassifications. Start at the top with the checking account balance or whatever is the first account on the trial balance.
Recall that an original source can be a formal document substantiating a transaction, such as an invoice, purchase order, cancelled check, or employee time sheet. Not every transaction produces an original source document that will alert the bookkeeper that it is time to make an entry. If you haven’t decided whether to use cash or accrual basis as the timing of documentation for your small business accounting, our guide on the basis of accounting can help you decide. Liabilities also include amounts received in advance for a future sale or for a future service to be performed. You will learn more about depreciation and its computation inLong-Term Assets. However, one important fact that we needto address now is that the book value of an asset is notnecessarily the price at which the asset would sell.
